Project website: https://alf.physik.uni-wuerzburg.de/.
-> Interested contributors please check our CONTRIBUTING.md guidelines.
-> This is the development version of ALF, the latest stable version is ALF 2.6.
Description
The **A**lgorithms for **L**attice **F**ermions package provides a general code for the finite temperature and projective auxiliary field Quantum Monte Carlo algorithm. The code is engineered to be able simulate any model that can be written in terms of sums of single body operators, of squares of single body operators and single body operators coupled to an Ising field with given dynamics. We provide predefined types that allow the user to specify the model, the Bravais lattice as well as equal time and time displaced observables. The code supports an MPI implementation. Examples such as the Hubbard model, the SU(N) Kondo lattice model, tV models, models with long ranged interactions as well as Z2 lattice gauge theories coupled to fermions adn Z2 matter are discussed in the documentation. Slides on the auxiliary field QMC can be found here.
The Hamiltonians we can consider read:
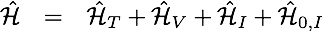
where
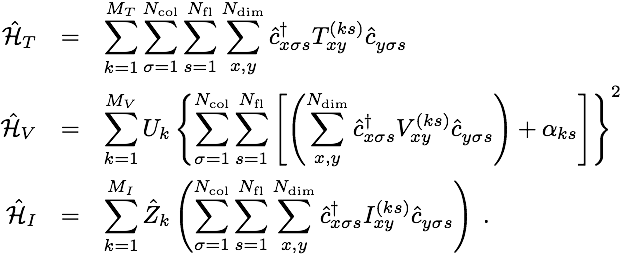
Here Z denotes a scalar field (Ising or real continuous field) with predefined dynamics. If your model can be written in this form then it will be amenable to the ALF.
pyALF
For ease of use, pyALF provides a Python interface to run the ALF code.
Doxygen
You can find here Doxygen formatted documentation. (Work in progress)
Installation
- Please check the latest documentation for more details and Sec. 6.1, "Quick Start", to try ALF out straight away.
PREREQUISITES
- Make
- A Fortran compiler, such as gfortran or ifort
- Blas+Lapack libraries
- Python3
- MPI libraries (optional)
- For HDF5 (optional)
- C++ preprocessor (default: g++)
- Curl
- gzip development libraries
Alternatively, one could use this Docker image, which has ALF, pyALF and a Jupyter server pre-installed.
Linux
To install the relevant packages.Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint:
sudo apt install make gfortran libblas-dev liblapack-dev \python3 libopenmpi-dev g++ curl libghc-zlib-dev gitRed Hat/Fedora/CentOS:
sudo yum install make gfortran libblas-devel liblapack-devel \python3 libopenmpi-dev g++ curl zlib gitOpenSuSE/SLES:
sudo zypper install make gcc-fortran lapack-devel \python3 libopenmpi-devel gcc-c++ curl zlib-devel gitArch Linux:
sudo pacman -S make gcc-fortran lapack python3 openmpi curl zlib git- Other Unixes
gfortran and the lapack implementation from netlib.org should be available for your system. Consult the documentation of your system on how to install the relevant packages. The package names from linux should give good starting points for your search. - MacOS
gfortran for MacOS can be found at https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/GFortranBinaries#MacOS. Detailed information on how to install the package can be found at: https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/GFortranBinariesMacOS. You will need to have Xcode as well as the Apple developer tools installed. - Windows
The easiest way to compile ALF in Windows is trough the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). It allows to run Linux within Windows. You can install the WSL and follow the instructions for Linux.
Compiling and running
- Source configure.sh to set the necessary environment variables. Type ./configure.sh to browse through a list of options. Notice that directory names containing spaces are not supported.
- Compile with make: The command make all compiles both the analysis and Monte Carlo binaries. To remove previously created and possibly conflicting binaries, it might make sense to first run make clean.
- Prepare Simulation directory: A simulation directory must contain the two following files:
- seeds containing seeds for the random number generator
- parameters containing the simulation parameters See the example directory Scripts_and_Parameters_files/Start/.
- Run ALF.out created during the compilation in folder Prog/. Be sure that you current working directory is the one that contains seeds and parameters.
Quick start
The following lines cover the minimal steps of fulfilling the prerequisites (on a Debian-based system), obtaining the source code, compiling the program, running a simulation and analyzing the results.
FILES AND DIRECTORIES
Libraries Libraries. Once that the environment is set in the file configure.sh the Libraries can be compiled with the make command.
Prog Main program and subroutines.
Analysis Analysis programs.
Scripts_and_Parameters_files Helper scripts and the Start/ directory, which contains the files required to start a run.
Documentation We have included in the file doc.pdf an extensive documentation.
testsuite An automatic test suite for various parts of the code
TESTING
We have about 30 tests that test various parts of the program in the folder testsuite. As testing framework we employ CTest. To run the tests, the ALF package must first be compiled. The following commands compile ALF in a minimal setup and run the tests.
LICENSE
The various works that make up the ALF project are placed under licenses that put a strong emphasis on the attribution of the original authors and the sharing of the contained knowledge. To that end we have placed the ALF source code under the GPL version 3 license and took the liberty as per GPLv3 section 7 to include additional terms that deal with the attribution of the original authors (see license.GPL and license.additional). The Documentation of the ALF project by the ALF contributors is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (see Documentation/license.CCBYSA). Note that we link against parts of lapack, which is licensed under a BSD license (see license.lapack).
KNOWN ISSUES
We have detected a bug in both 2017 versions of Intel's MPI implementation (mpi.intel/2017(default) and mpi.intel/2017.2) if used in combination with the parallel (threaded) MKL library. The advise is to use either the 2016 suite (intel/16.0 (compiler), mpi.intel/5.1 and mkl/11.3 ) or the new 2018 suite (intel/18.0 (compiler), mpi.intel/2018 and mkl/2018). We did not detect this issue in both environments. You should also be aware the by default, dynamic linking is used. Hence if you use the 2016 or 2018 modules at compilations, the bug can reenter if you still load the 2017 versions at runtime. So please adapt your configureHPC.sh as well as your Jobfiles for the loadleveler accordingly. Additional note: In the serial version, the bug also seems to be absent. If you want to use the 2017 suite, you have to use the serial version of MKL (mkl/2017_s), which means you cannot profit from openMP multi-threading. This library is linked statically, hence taking care of this at compile time is sufficient and there is no need to adapt the Jobfiles. WARNING: Even if you do not use parallel tempering actively, we still strongly suggest to take care of the above bug as it is extremely hard to estimate hidden influences and correlations of this memory allocation bug in the rest of the program. It is possible the other parts of the algorithm might be affected apart from the tempering exchange step even so we have absolutely no hint of additionally affected sections in ALF.
Intel suite 2017: Apparently, there seems to be a bug in the Intel MPI threaded memory allocator if both Intel MPI implementation and the PARALLEL version of MKL is used. This bug corrupts the data transmission during tempering moves such that the Monte Carlo is broken. The current advise is to either use an earlier version (2016 and before) or a newer one (2018 and later). It should also be OK to use the sequential MKL library if openMP multi-threading is not required. Setting the environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 however does not fix the bug as this still uses the threaded MKL library (Date: 1. June 2018)
Generated by

 )
)